Collateral and risk integration: why now?
03 November 2021
Sophie Marnhier-Foy, director, product strategy at Adenza, explains that regulatory changes are pushing market participants to meet a new level of sophistication regarding risk metrics and collateral exposure calculations
 Image: stock.adobe.com/WrightStudio
Image: stock.adobe.com/WrightStudio
In the context of Uncleared Margin Rules (UMR) and Basel Framework adoption, firms need to comply with a set of interdependent new regulations and optimise the corresponding total cost of ownership (TCO) impact. Market best practices around counterparty credit risk management are also quickly evolving. In terms of risk, clearing, margin, and collateral management functions and their integration, now is the time for organisations to position themselves for change.
Why now?
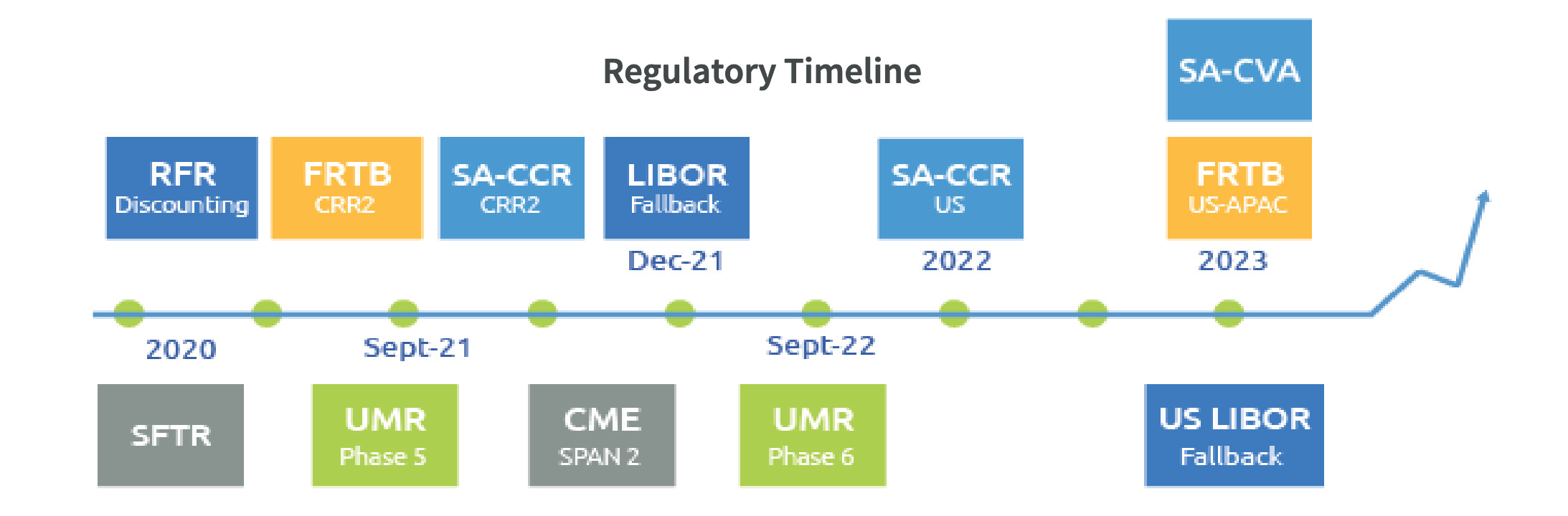
These multiple regulation changes will compel financial institutions to reach a new level of sophistication within a tight timeframe. It defines new derivatives exposure metrics (Standardised Approach - Counterparty Credit Risk, SA-CCR), new initial margin collateral (UMR), and a fundamental review of market risk capital charges (Fundamental Review of the Trading Book, FRTB).
For firms to manage the active global regulatory roll-out depicted in the regulatory timeline, this requires a new level of sophistication covering these new risk metrics, risk management, and collateral exposure calculations. Influenced by the evolving regulatory mandates, new market best practices around counterparty credit risk are also emerging. In parallel, clearing programmes are expanding, adding new approaches for capital optimisation and margin efficiency. Firms will need to institute much more robust collateral management systems to incorporate this expansion.
Taking a tactical approach to regulatory adoption may result in operational risk, inefficiencies, and increased costs. Indeed, relying upon a fragmented approach will require firms to update many systems, resulting in duplication of effort and increasing the TCO for regulatory requirements that are here to stay.
Therefore, reassessing the firm’s current risk systems is imperative to developing a strong strategic approach that simplifies operational challenges.
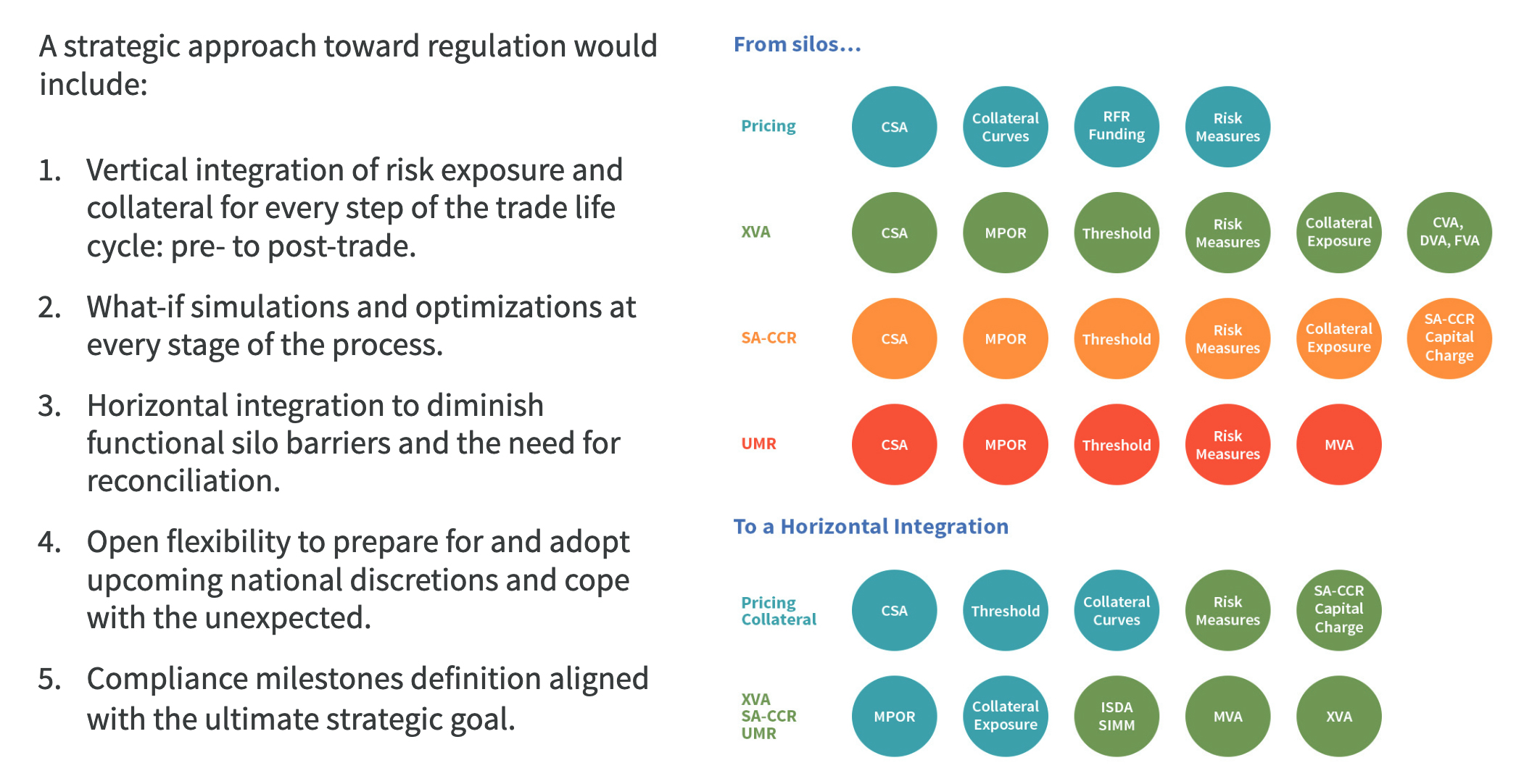
Collateral, post-trade processing and risk integration: A must-have to turn a mandatory exercise into a business benefit
The foundation of an optimised collateral implementation definitively starts with a complete integration between securities inventory, margin exposures, collateral processes, and tri-party settlement – in real time. The resulting holistic view leads to inventory optimisation and collateral cost reduction. Driving collateral fluidity, transformation, and optimisation is strategic. But is that enough to efficiently optimise collateral and reach compliance with new regulations and new market requirements around counterparty credit risk, now and beyond?
Requirements have changed and expanded and the pressure on collateral costs is increasing.
The most advanced institutions don’t simply allocate, they anticipate and optimise before exchanging collateral. They recognise that simulations are required pre and post-trade and must include detailed collateral inputs. Thus, the marketplace now considers the need for complete what-if collateral, margin, and capital charge simulations to be imperative, fully integrated in a single platform.In this current environment of increased regulatory requirements, with its amplified focus on counterparty credit risk and market fluctuations, new best practices are also emerging around the integration of collateral and risk.
Drivers for risk and collateral integration
The Basel Framework is one of the most significant post-crisis reforms and covers a vast array of regulations – the so-called ‘Basel IV’, FRTB, UMR, Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR), Internal Capital and Liquidity Adequacy Assessment Process (ICLAAP), and others.
This has increased the need for high-quality liquid assets (HQLA) to cover liquidity risk and redefined the amount of capital required to cover counterparty credit risk exposures. For instance, additional amounts of capital are required for non-centrally cleared derivatives with long maturities and insufficient collateral.
It has also increased the demand for collateral for cleared and uncleared trades. Basel IV changes the entire dynamic of the trading process, as each transaction now generates collateral and capital costs. The increase in clearing volumes also generates new collateral flows.
In parallel, the collateral exposure used to determine the collateral to call or deliver is now based on more complex risk calculations. Indeed, the market has shifted from a simple market-value based exposure to value at risk (VaR) and sensitivity-based initial margin (IM) calculations for cleared and uncleared OTC derivatives. Those new risk metrics are not additive; each needs to be adjusted, simulated, and recalculated very quickly – often intraday.
At the trade level, these new regulatory charges have created a new “total cost” of the trade. Interestingly, an analysis of this new total cost and the related new regulatory risk metrics reveals a common denominator – and that is collateral. The parameters and exposures of collateral are key inputs to the risk calculation of SA-CCR, Monte Carlo potential future exposure (MC PFE), credit valuation adjustment (CVA), margin valuation adjustment (MVA), and so on.
In 2020, risk and collateral interdependencies were highlighted due to market volatility. Indeed, under those conditions, the margin procyclicality effect could generate unmanageable collateral calls:
when market risk increases, margin and collateral requirements increase. Under such circumstances, procyclicality mitigation tools will be required. How better to do that than in an integrated risk and collateral platform?
What does integration mean for financial institutions?
Firms need an approach where managing collateral is not a sequential process, but rather the centerpiece of the solution.
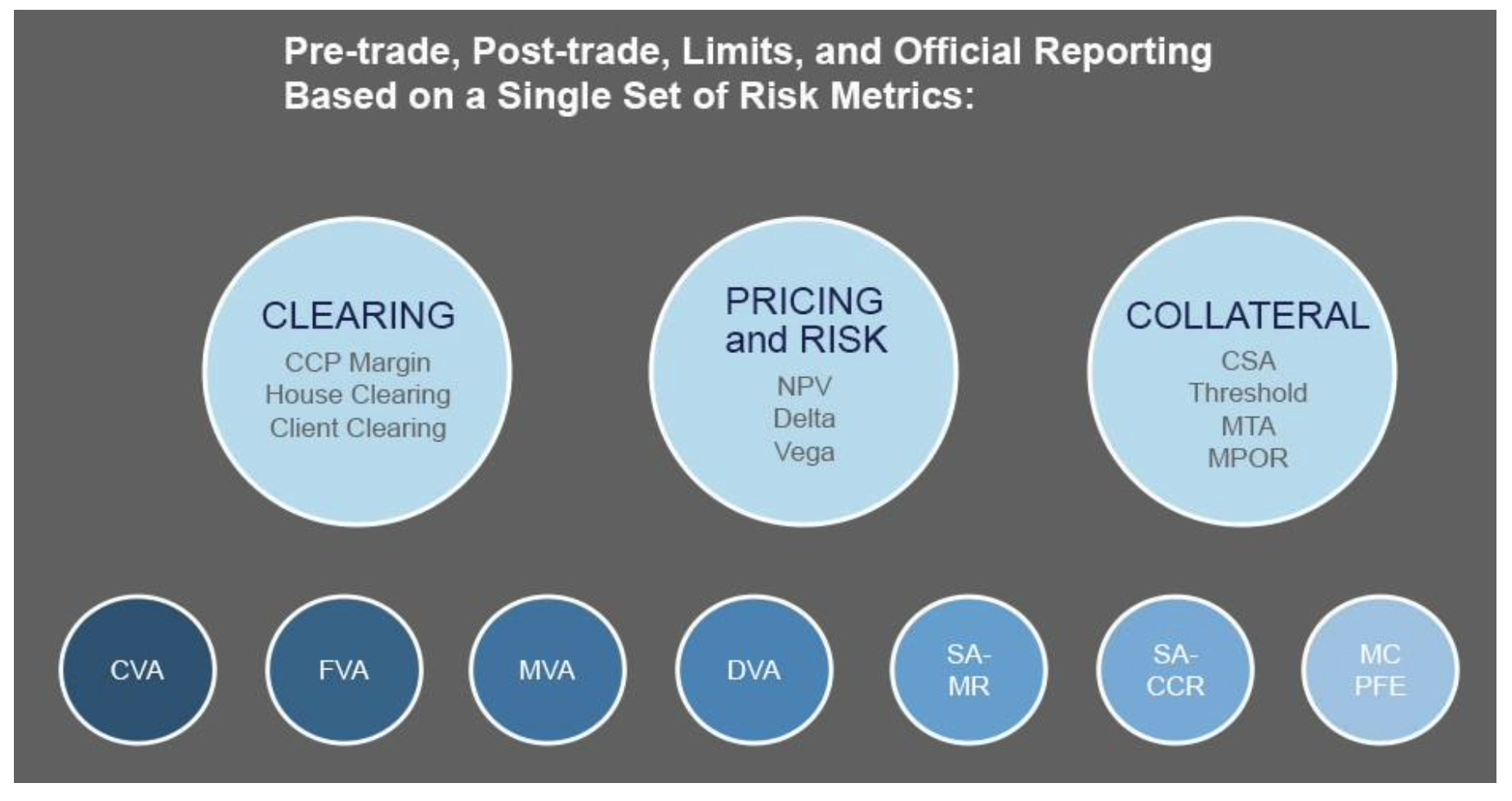
As represented by the diagram, an ultimate solution integrates collateral parameters, collateral exposure, securities and cash inventory, risk metrics, and margin calculation.
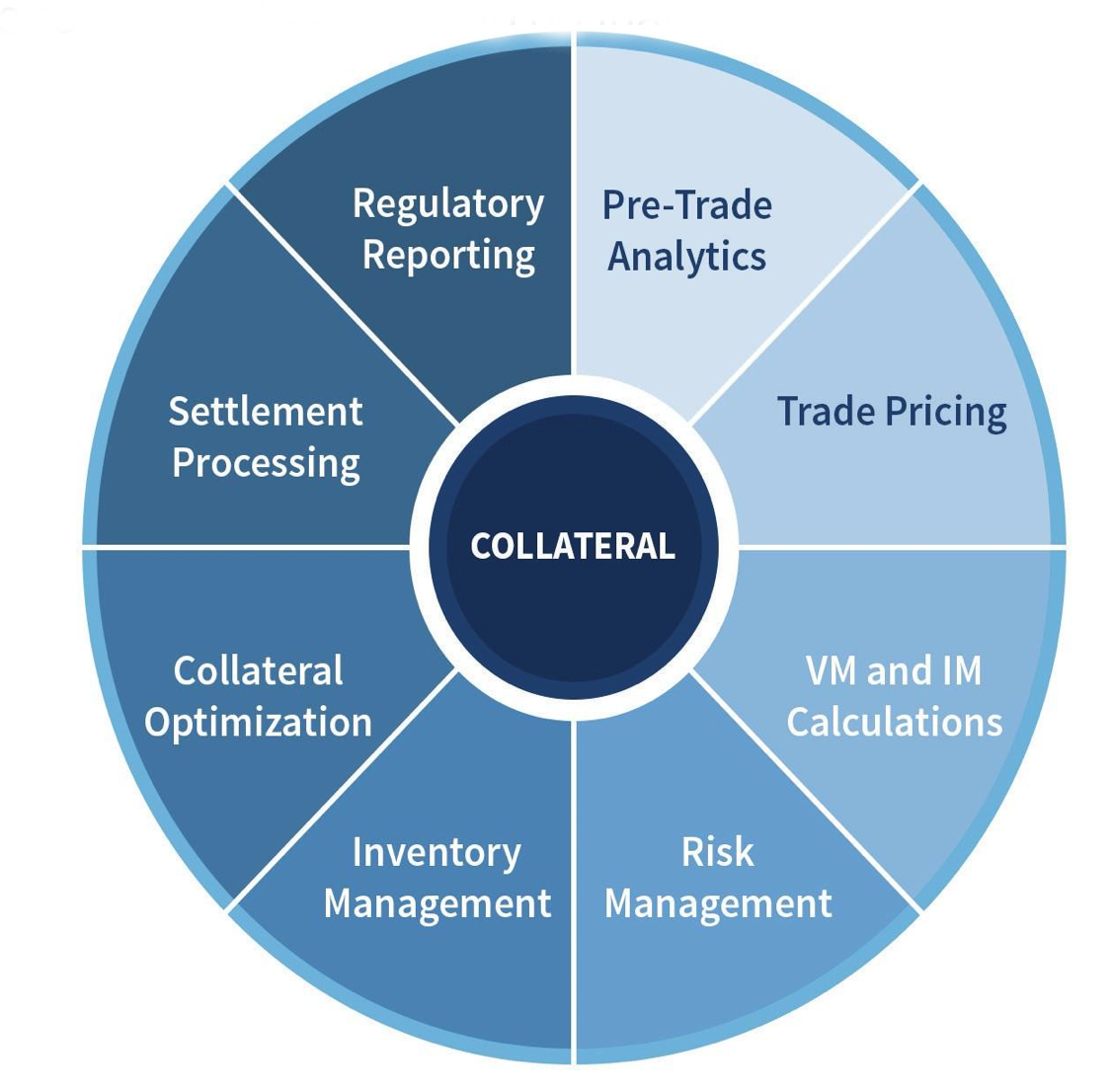
Optimisation needs to be integrated at every stage of the trade lifecycle
Beyond the need for an integrated risk and collateral solution, organisations need to completely rethink optimisation use cases. Usually considered in isolation, use cases can be asynchronous and therefore apply at every stage of a trade lifecycle because:
• Traders need to anticipate the impact of new regulations upfront.
• Collateral managers continually strive to assess the impact of new regulations on future margin calls.
• Risk managers must forecast clearing, credit, and market risk exposures ahead of regulatory milestones.
Viewing collateral and regulatory risk compliance as a sequential process – downstream from trade negotiation and execution – is a thing of the past. In contrast, regulatory compliance and optimisation must now start before trades are negotiated, sometimes months before!
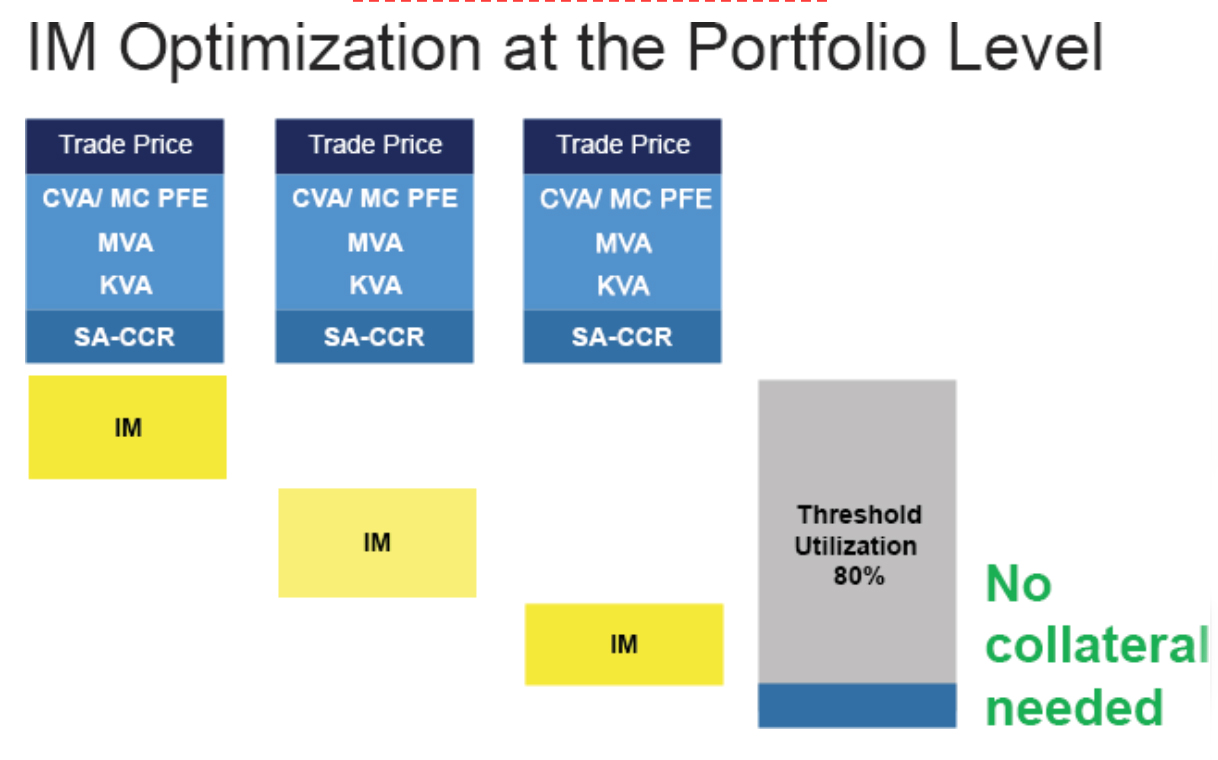
The recent UMR preparation exercise is a good illustration. Hundreds of firms fell under UMR compliance in September 2021 as part of the UMR Phase 5 milestones (all firms with AANA greater than US$50 billion). Many of those firms have been proactively anticipating their collateral needs to avoid exchanging collateral altogether. How is this possible? The regulation allows firms to not exchange collateral if the total IM exposure is below the UMR threshold. Reducing the collateral to zero is clearly the best optimisation. But, for that to happen, it must take place before the trade is booked. In fact, most firms are running simulations months in advance, using legacy portfolios to anticipate and manage their UMR threshold.
Regulatory compliance and collateral input are also part of the mix during the clearing novation process, where the headroom check process includes VaR, sensitivities, and unsettled collateral. For central counterparties (CCPs), collateral and risk integration at every stage of the lifecycle has long been required; they are mandated to calculate risk in less than 10 seconds, including collateral inputs.
With the adoption of new regulatory metrics like SA-CCR, the expansion of clearing volumes, and UMR regulatory IM, implementing a risk and collateral integration is mission critical to stay competitive.
UMR THRESHOLD OPTIMIZATION
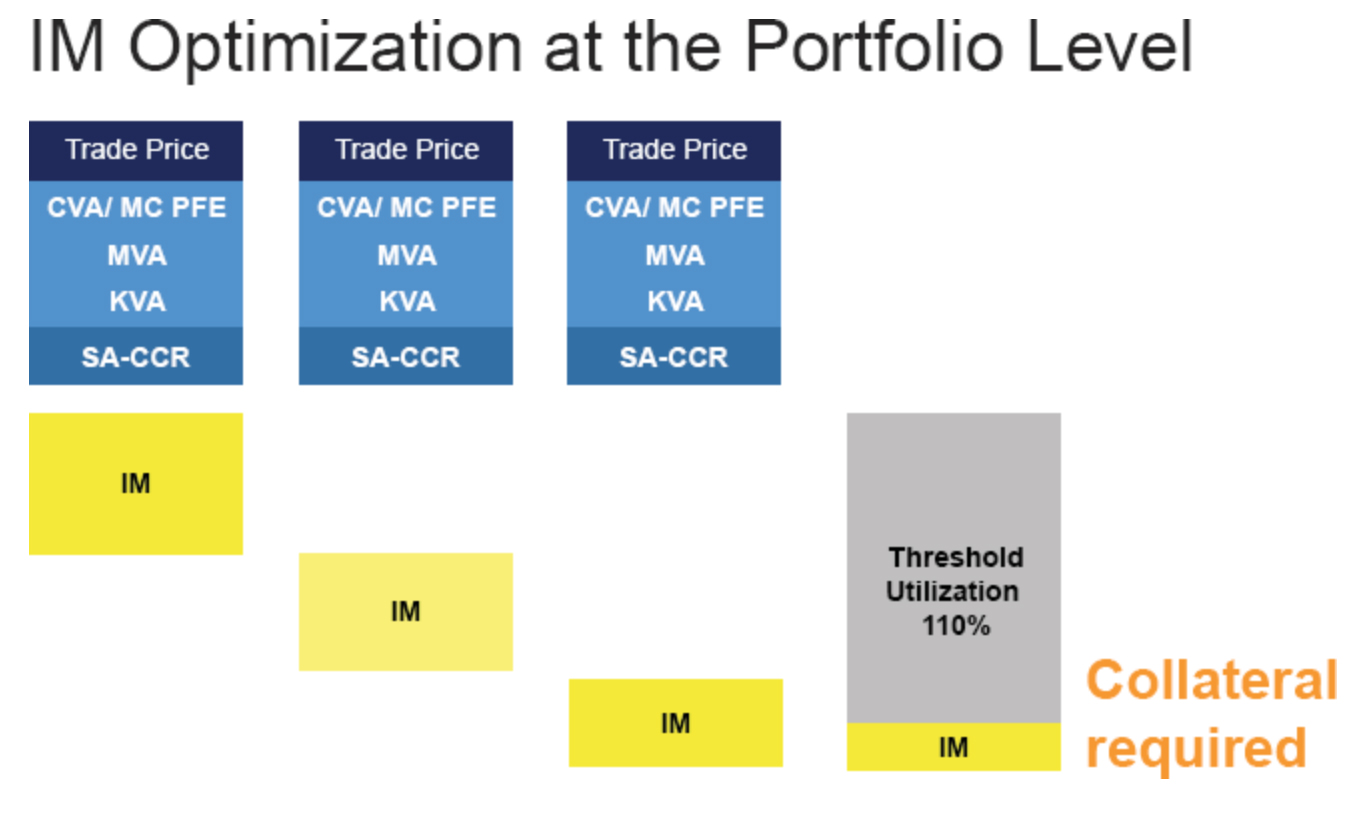
The list of what-if simulations is long and can be leveraged by an integrated solution
The powerful benefits brought by incorporating pre-trade simulations in an integrated solution include:
• Identifying the cheapest clearing venue to minimise total IM and related collateral costs that take the existing portfolio into account.
• Comparing the cost of not clearing vs clearing by comparing a standard initial margin model (SIMM) margin to a CCP margin.
• Analysing the impact of a credit support annex (CSA) threshold into a CVA charge.
• Understanding how the margin period of risk (MPOR) will affect the SA-CCR for a selected counterparty.
Now is time to plan for a platform change and target optimal consolidation and efficiency beyond compliance
In summary, in the context of regulatory compliance and beyond – and starting now – firms need an integrated collateral and risk platform in an optimised framework that must include:
• An integrated front-to-back solution with real-time exposures and inventory.
• A solid but flexible risk engine.
• A holistic approach to risk and collateral without sequential steps – where collateral is risk, and risk is collateral.
After dealing with pandemic-driven disruptions, firms today seek to build agile operating foundations. They know that they will continue to need to deal with the unknown and unexpected.
Calypso’s one-stop shop for regulation, risk, and collateral is an excellent place to start.
Why now?
These multiple regulation changes will compel financial institutions to reach a new level of sophistication within a tight timeframe. It defines new derivatives exposure metrics (Standardised Approach - Counterparty Credit Risk, SA-CCR), new initial margin collateral (UMR), and a fundamental review of market risk capital charges (Fundamental Review of the Trading Book, FRTB).
For firms to manage the active global regulatory roll-out depicted in the regulatory timeline, this requires a new level of sophistication covering these new risk metrics, risk management, and collateral exposure calculations. Influenced by the evolving regulatory mandates, new market best practices around counterparty credit risk are also emerging. In parallel, clearing programmes are expanding, adding new approaches for capital optimisation and margin efficiency. Firms will need to institute much more robust collateral management systems to incorporate this expansion.
Taking a tactical approach to regulatory adoption may result in operational risk, inefficiencies, and increased costs. Indeed, relying upon a fragmented approach will require firms to update many systems, resulting in duplication of effort and increasing the TCO for regulatory requirements that are here to stay.
Therefore, reassessing the firm’s current risk systems is imperative to developing a strong strategic approach that simplifies operational challenges.


Collateral, post-trade processing and risk integration: A must-have to turn a mandatory exercise into a business benefit
The foundation of an optimised collateral implementation definitively starts with a complete integration between securities inventory, margin exposures, collateral processes, and tri-party settlement – in real time. The resulting holistic view leads to inventory optimisation and collateral cost reduction. Driving collateral fluidity, transformation, and optimisation is strategic. But is that enough to efficiently optimise collateral and reach compliance with new regulations and new market requirements around counterparty credit risk, now and beyond?
Requirements have changed and expanded and the pressure on collateral costs is increasing.
The most advanced institutions don’t simply allocate, they anticipate and optimise before exchanging collateral. They recognise that simulations are required pre and post-trade and must include detailed collateral inputs. Thus, the marketplace now considers the need for complete what-if collateral, margin, and capital charge simulations to be imperative, fully integrated in a single platform.In this current environment of increased regulatory requirements, with its amplified focus on counterparty credit risk and market fluctuations, new best practices are also emerging around the integration of collateral and risk.
Drivers for risk and collateral integration
The Basel Framework is one of the most significant post-crisis reforms and covers a vast array of regulations – the so-called ‘Basel IV’, FRTB, UMR, Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR), Internal Capital and Liquidity Adequacy Assessment Process (ICLAAP), and others.
This has increased the need for high-quality liquid assets (HQLA) to cover liquidity risk and redefined the amount of capital required to cover counterparty credit risk exposures. For instance, additional amounts of capital are required for non-centrally cleared derivatives with long maturities and insufficient collateral.
It has also increased the demand for collateral for cleared and uncleared trades. Basel IV changes the entire dynamic of the trading process, as each transaction now generates collateral and capital costs. The increase in clearing volumes also generates new collateral flows.
In parallel, the collateral exposure used to determine the collateral to call or deliver is now based on more complex risk calculations. Indeed, the market has shifted from a simple market-value based exposure to value at risk (VaR) and sensitivity-based initial margin (IM) calculations for cleared and uncleared OTC derivatives. Those new risk metrics are not additive; each needs to be adjusted, simulated, and recalculated very quickly – often intraday.
At the trade level, these new regulatory charges have created a new “total cost” of the trade. Interestingly, an analysis of this new total cost and the related new regulatory risk metrics reveals a common denominator – and that is collateral. The parameters and exposures of collateral are key inputs to the risk calculation of SA-CCR, Monte Carlo potential future exposure (MC PFE), credit valuation adjustment (CVA), margin valuation adjustment (MVA), and so on.
In 2020, risk and collateral interdependencies were highlighted due to market volatility. Indeed, under those conditions, the margin procyclicality effect could generate unmanageable collateral calls:
when market risk increases, margin and collateral requirements increase. Under such circumstances, procyclicality mitigation tools will be required. How better to do that than in an integrated risk and collateral platform?
What does integration mean for financial institutions?
Firms need an approach where managing collateral is not a sequential process, but rather the centerpiece of the solution.
As represented by the diagram, an ultimate solution integrates collateral parameters, collateral exposure, securities and cash inventory, risk metrics, and margin calculation.

Optimisation needs to be integrated at every stage of the trade lifecycle
Beyond the need for an integrated risk and collateral solution, organisations need to completely rethink optimisation use cases. Usually considered in isolation, use cases can be asynchronous and therefore apply at every stage of a trade lifecycle because:
• Traders need to anticipate the impact of new regulations upfront.
• Collateral managers continually strive to assess the impact of new regulations on future margin calls.
• Risk managers must forecast clearing, credit, and market risk exposures ahead of regulatory milestones.
Viewing collateral and regulatory risk compliance as a sequential process – downstream from trade negotiation and execution – is a thing of the past. In contrast, regulatory compliance and optimisation must now start before trades are negotiated, sometimes months before!
The recent UMR preparation exercise is a good illustration. Hundreds of firms fell under UMR compliance in September 2021 as part of the UMR Phase 5 milestones (all firms with AANA greater than US$50 billion). Many of those firms have been proactively anticipating their collateral needs to avoid exchanging collateral altogether. How is this possible? The regulation allows firms to not exchange collateral if the total IM exposure is below the UMR threshold. Reducing the collateral to zero is clearly the best optimisation. But, for that to happen, it must take place before the trade is booked. In fact, most firms are running simulations months in advance, using legacy portfolios to anticipate and manage their UMR threshold.
Regulatory compliance and collateral input are also part of the mix during the clearing novation process, where the headroom check process includes VaR, sensitivities, and unsettled collateral. For central counterparties (CCPs), collateral and risk integration at every stage of the lifecycle has long been required; they are mandated to calculate risk in less than 10 seconds, including collateral inputs.
With the adoption of new regulatory metrics like SA-CCR, the expansion of clearing volumes, and UMR regulatory IM, implementing a risk and collateral integration is mission critical to stay competitive.
UMR THRESHOLD OPTIMIZATION


The list of what-if simulations is long and can be leveraged by an integrated solution
The powerful benefits brought by incorporating pre-trade simulations in an integrated solution include:
• Identifying the cheapest clearing venue to minimise total IM and related collateral costs that take the existing portfolio into account.
• Comparing the cost of not clearing vs clearing by comparing a standard initial margin model (SIMM) margin to a CCP margin.
• Analysing the impact of a credit support annex (CSA) threshold into a CVA charge.
• Understanding how the margin period of risk (MPOR) will affect the SA-CCR for a selected counterparty.
Now is time to plan for a platform change and target optimal consolidation and efficiency beyond compliance

In summary, in the context of regulatory compliance and beyond – and starting now – firms need an integrated collateral and risk platform in an optimised framework that must include:
• An integrated front-to-back solution with real-time exposures and inventory.
• A solid but flexible risk engine.
• A holistic approach to risk and collateral without sequential steps – where collateral is risk, and risk is collateral.
After dealing with pandemic-driven disruptions, firms today seek to build agile operating foundations. They know that they will continue to need to deal with the unknown and unexpected.
Calypso’s one-stop shop for regulation, risk, and collateral is an excellent place to start.
NO FEE, NO RISK
100% ON RETURNS If you invest in only one securities finance news source this year, make sure it is your free subscription to Securities Finance Times
100% ON RETURNS If you invest in only one securities finance news source this year, make sure it is your free subscription to Securities Finance Times



